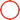
A ball valve is a type of valve that opens and closes by rotating a ball. Its core structure and working principle are as follows:
-
Ball
- A rotating component with a through-hole, typically made of stainless steel, brass, or plastic/ceramic.
- O-type ball valve: The ball's hole diameter matches the pipeline.
- V-type ball valve: Features a V-shaped notch for flow regulation.
-
Seat
- Contacts the ball to ensure sealing, with materials selected based on the medium (e.g., PTFE, metal, or ceramic).
- Floating ball valve: Relies on medium pressure to press the seat against the ball.
- Fixed ball valve: Uses spring preload to maintain sealing.
-
Stem
- Connects the ball to the actuator, transmitting torque. Made of corrosion-resistant materials.
-
Body
- Supports internal components, available in one-piece, two-piece, or three-piece designs.
- Materials must be compatible with the medium (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel).
-
II. Typical Structural Types
- Floating Ball Valve: The ball is free-floating, suitable for low-to-medium pressure applications, using downstream single-side sealing via medium pressure.
- Fixed Ball Valve: The ball is secured by upper and lower shafts, ideal for high-pressure and large-diameter applications, with bidirectional sealing.
- V-Type Ball Valve: Features a V-shaped cutout for precise flow control, suitable for fibrous or particulate media.
- Orbital Ball Valve: The ball rotates while simultaneously lifting, reducing seal wear, ideal for high-viscosity fluids.
-
III. Working Principle
The valve opens or closes by rotating the stem 90°, aligning the ball's hole with the pipeline (open) or perpendicular to it (closed).
- O-type ball valve: Provides a fully unobstructed flow path when open.
- V-type ball valve: Adjusts flow via the angle of the V-notch.
-
IV. Special Designs
- Wafer Ball Valve: Uses a one-piece cast body with a wedge-shaped seal, allowing for online maintenance.
- Eccentric Ball Valve: The valve stem is offset from the ball's centerline, reducing seal wear during operation.
- For a more intuitive breakdown, refer to dynamic diagram sets or 3D animations. Let me know if you need further refinements!