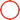
1. Basic DefinitionA butterfly valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve that uses a disc-shaped closure element to regulate or isolate fluid flow. The disc rotates 90 degrees within the pipe bore to open or close the flow path, resembling the wings of a butterfly - hence its name.
2. Key Components
-
Disc: The primary flow control element, typically circular in shape
-
Stem: Connects the actuator to the disc for rotational movement
-
Seat: Provides sealing between the disc and valve body
-
Body: Main pressure-containing structure that fits between pipe flanges
3. Working PrincipleIn operation:
-
Open position: Disc aligns parallel to flow direction (minimal pressure drop)
-
Closed position: Disc rotates perpendicular to block flow completely
-
Intermediate positions: Allow flow regulation (in some designs)
4. Main Types
-
Concentric: Most common, with stem centered in disc
-
Double-eccentric: Offset stem reduces operating torque
-
Triple-eccentric: Advanced design for high-pressure applications
5. Material OptionsCommon materials include:
-
Body: Cast iron, ductile iron, carbon steel, stainless steel
-
Disc: Stainless steel, aluminum bronze, nickel alloys
-
Seat: EPDM, Viton, PTFE, metal-to-metal
6. Advantages
-
Compact, lightweight design
-
Quick operation (90° rotation only)
-
Lower cost compared to other valve types
-
Minimal maintenance requirements
-
Suitable for large diameter pipes
7. Common Applications
-
Water and wastewater treatment
-
Chemical processing
-
Power generation
-
HVAC systems
-
Oil and gas pipelines
-
Food and beverage industry
8. Selection ConsiderationsWhen choosing a butterfly valve:
-
Pressure and temperature requirements
-
Flow characteristics needed
-
Media compatibility
-
Actuation method (manual, electric, pneumatic)
-
Industry standards compliance (API, ANSI, ISO)