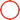
1. Fundamental Definition & Structural Composition
A ball valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve characterized by a spherical disc (the ball) with a precision-drilled through-bore. This rotating ball, actuated by a stem connected to manual levers or automated actuators, provides exceptional shut-off capability in pipelines carrying liquids, gases, or multiphase media.
Core Components:
-
Ball: Typically stainless steel (ASTM A351 CF8M) or chrome-plated for corrosion resistance
-
Seats: PTFE, reinforced thermoplastics, or metal-to-metal for high-temperature applications
-
Stem: ASTM A182 F6a with blowout-proof design
-
Body: Cast/machined per ASME B16.34 standards
2. Operational Mechanics & Performance Metrics
2.1 Working Principle
The valve achieves flow regulation through 90° rotation:
-
0° (Open): Bore aligns with pipeline axis, offering minimal flow restriction (Cv ≈ 50% higher than gate valves)
-
90° (Closed): Bore becomes perpendicular, with seats forming bidirectional bubble-tight seals (leakage rate ≤ 100 ppm per API 598)
2.2 Key Performance Indicators
|
Parameter |
Standard Range |
|---|---|
|
Pressure Rating |
ANSI 150~2500 (PN 20~420) |
|
Temperature Range |
-196°C (cryogenic) to 650°C (special alloys) |
|
Actuation Torque |
20~800 Nm (varies with size/pressure) |
3. Industrial Taxonomy & Selection Criteria
3.1 Design Variants
-
Floating vs Trunnion-mounted: For ≤DN300 (floating) vs high-pressure large-bore (trunnion)
-
Full/Reduced Port: 100% bore for pigging vs 80% for throttling
-
Multiport Configurations: 3-way L/T pattern for flow diversion
3.2 Material Compatibility Matrix
|
Media |
Recommended Material |
|---|---|
|
HCl ≤ 30% |
Hastelloy C276 |
|
Superheated Steam |
ASTM A217 WC9 |
|
Abrasive Slurries |
Tungsten carbide-coated |
4. Sector-Specific Applications
-
Oil & Gas: Subsea X-mas trees (API 6DSS compliant)
-
Pharma: CIP/SIP-capable ultra-clean designs (ASME BPE)
-
Nuclear: SIL3-certified actuators for ECCS
5. Maintenance & Failure Prevention
-
Common Issues: Seat erosion (mitigated by stellite hardening)
-
Fugitive Emissions: ISO 15848-1 compliant stem seals
-
Fire Safety: API 607/6FA fire-tested designs